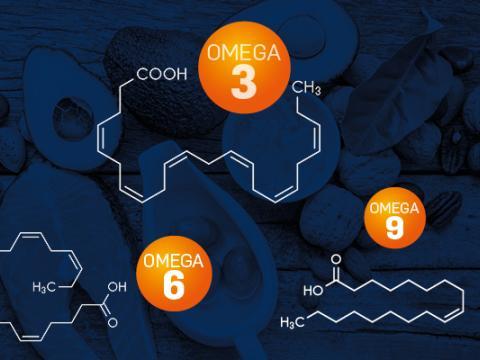
Each fatty acid has a specific role in certain body functions. The precursors of omega-3 and omega-6 activate enzymes which trigger biochemical reactions resulting in the synthesis of long-chain fatty acids, for instance Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), Gamma-Linolenic acid (GLA), Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA), Arachidonic acid (AA), etc.

Numerous studies have revealed the specific role of DHA omega-3 in some disorders. For example, a link has been established between emotional instability and omega-3 deficiency. Other studies have highlighted the role of omega-3 in brain plasticity, controlling neuroinflammation, therefore reducing cognitive disorders, and preventing stress, anxiety and depression1.
The role of DHA (docosahexaenoic acid)
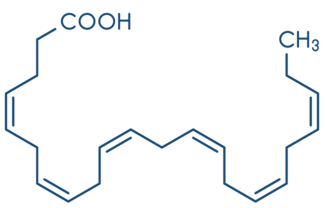
DHA omega-3 fatty acids are the constituents of nerve cells and have a major role in membrane structure. They contribute to synaptic transmission and are also involved in brain and retina functions and development.
DHA has a more specific role in memory functions. It is involved in nerve signal transmission. A study of 12,000 men and women has shown a correlation between consumption of DHA in food and a smaller reduction in cognitive performance2 .
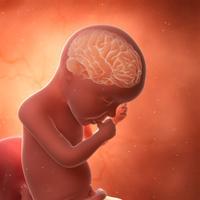
Oméga 3 de type DHA et développement cérébral du fœtus
Le DHA intervient dans le développement du système nerveux et de la rétine du bébé. Le DHA se met en réserve dans le tissu adipeux du bébé pour terminer le développement cérébral après la naissance contrairement au bébé singe qui a terminé son développement cérébral à la naissance. Augmenter sa consommation en Oméga 3 pendant la grossesse est donc conseillé.
DHA omega-3 and fetal brain development DHA is involved in the development of the nervous system and retina in babies.
DHA is stored in fatty tissue in human babies to complete brain development after birth in contrast with infant monkeys whose brains are completely developed at birth. Increasing omega-3 consumption during pregnancy is therefore recommended.
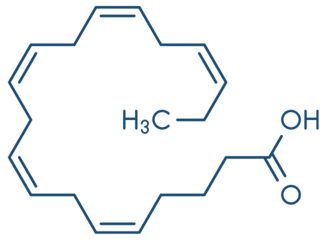
Le rôle de l’EPA (acide eicosapentaénoïque)
Omega-3 fatty acids are precursors of anti-inflammatory substances which are part of the prostaglandin family. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is converted into PGE3 (prostaglandin E3) whose anti-inflammatory effects could be of interest in the treatment of inflammatory diseases such as arthritis, osteoarthritis, chronic inflammation, etc.
There is now acknowledged to be a close link between omega-3 and good cardiovascular function.
Where are DHA and EPA omega-3 fatty acids found?
DHA and EPA omega-3 fatty acids can be obtained solely from the diet. They are found in vegetable oils:
- Rapeseed oil
- walnut oil
- camelina oil
They are also contained in some foods which should be preferred:
- Oily fish such as mackerel, sardines or salmon
- walnuts