Chronic disease risks
Type-2 diabetes
Type-2 diabetes causes a chronic increase in blood glucose levels, which leads to a condition known as hyperglycaemia. An individual is more likely to develop type-2 diabetes when the sensitivity of their cells to insulin is reduced (known as insulin resistance).
Insulin is a pancreatic hormone which helps the body’s cells utilise glucose and thus helps to lower blood glucose levels. It is now known that overweight or obesity and/or excessive consumption of carbohydrates and sugars is a risk factor for insulin resistance.

Cardiovascular diseases
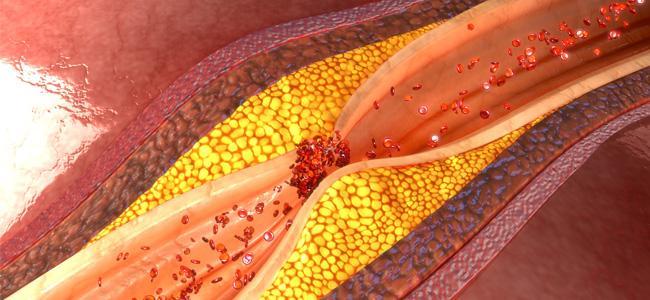
Cardiovascular disease is a term that covers all pathologies which relate to the process of atherosclerosis – during which fatty material (plaque) builds up in the arteries causing them to narrow and obstruct the blood flow. The consequences are: angina, cerebrovascular accident (stroke), heart failure, etc.
As with high blood pressure, age is the main risk factor for cardiovascular disease. However, once again, we know that being overweight, having a sedentary lifestyle and poor eating habits age the arteries more quickly, making them harder and facilitating the formation of atheromatous plaques (fatty deposits) in the arteries
Cancer
Overweight and obesity are recognised as risk factors for the development of certain types of cancer: breast cancer in post-menopausal women, endometrial cancer, ovarian cancer, cancer of the kidney, liver or bowel. Numerous studies have identified a link between excess body weight and an increase in the levels of several hormones, some of which are involved in the proliferation of cancer cells.
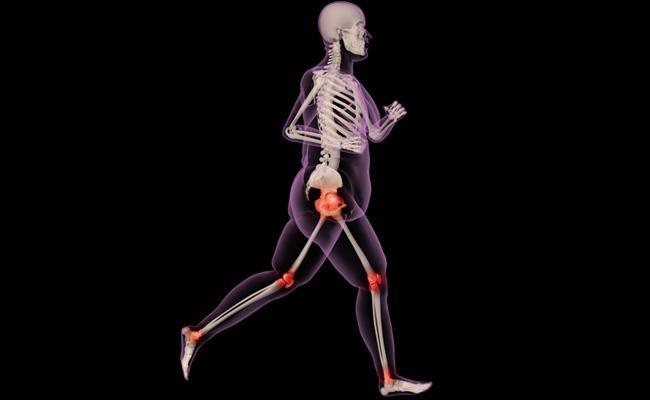
Osteoarthritis
Furthermore, it is also known that being overweight is a risk factor for osteoarthritis, not only of the hip and knee (i.e. the joints which must withstand the additional mechanical forces) but also of the hands and fingers. A number of studies have highlighted the adverse effects on the cartilage of certain cytokines secreted by the adipocytes (fat cells).
Overweight people produce excess amounts of these cytokines which contribute to the inflammation.
Sources :
- Website of the French National Cancer Institute (in French only): http://www.e-cancer.fr/Comprendre-prevenir-depister/Reduire-les-risques-de-cancer/Surpoids-et-obesite
- Website of the French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety products: https://www.anses.fr/en/content/sugar-food
- Richette P. Arthrose digitale La physiopathologie est plus complexe et s’enrichit de nouveaux concepts. La revue du praticien médecine générale Vol. 28, No. 929, November 2014.
